Hydroelectric energy uses the potential power of rivers. This is the most established renewable energy source, with nine of the ten largest power plants in the world. Three Gorges in China leads the way, with a capacity of 22.5 GWe, followed by Itaipu in Brazil, with fourteen GWe, and Xiluodu in China with thirteen. Hydroelectric plants provide grid stability by their large mechanical inertia.
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectric power plants rely on water to produce electricity. Water is the biggest renewable energy source. The water drops on turbine blades. The turbine converts the water's potential energy to kinetic energy. This then turns an electric generator. A dam is built across a river to obtain the water. The water is stored in large reservoirs and then released onto turbine propellers. The water is then re-released into the river in order to replenish the reservoir.

Hydroelectric power stations are normally built inside dams which impound rivers. When a flood occurs, a part of the dam serves as a spillway, turning turbines and generating electricity. The synchronous generators are powered by pumps that take water from rivers and other natural sources. Many communities have developed their own wind generators to harness the energy of moving water.
Photovoltaic (PV) technology
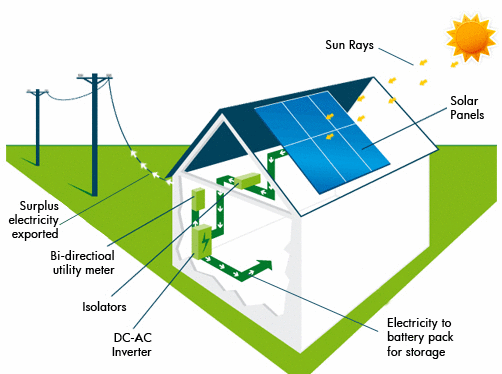
PV is a solar panel that generates electricity from sunlight. PV has numerous advantages over other types of energy sources, including reduced cost, low environmental impact, and long-term financial stability. However, PV only produces power during daylight hours, and the amount of electricity generated varies depending on the weather and season. Here's how PV can help increase energy security.
Photoelectric effect is the process by which photovoltaic cells convert sunlight to electricity. Photovoltaic cells are typically found on buildings' roofs. Utilities now build large photovoltaic farms. It takes five to 13 acres of land to generate a MW. Solar installations in the USA amounted to 16.7 GW. In other countries, there were another 2.2 GW.
Wind energy
Wind is the most abundant source of renewable energy in the world, providing more than five times as much power to humans. Wind turbines are the key components in wind energy production, as their rotor blades spin in a clockwise direction, collecting the energy. The turbine's nacelle houses a gearbox that converts wind energy into electricity. The electricity flows to a transformer that adjusts its voltage to the grid.

The process of wind energy is relatively simple and clean. It does away with the need for combustion and emits no greenhouse gases. It is also relatively inexpensive per kilowatt of energy produced, and requires little maintenance. Wind farms are often built in areas with weak winds, which are sparsely populated. Wind farms are built in isolated areas of the United States. This requires a detailed analysis to determine their feasibility.